Migrating Elastic Cloud Enterprise (ECE) clusters to new infrastructure is a critical task that demands meticulous planning and execution. Whether it’s to leverage new hardware, enhance performance, or meet evolving business needs, a successful migration ensures minimal downtime and data integrity. In this blog, we outline two recommended approaches for migrating your ECE clusters: creating an entirely new ECE installation or extending your existing installation across both data centers.
Option 1: Creating a New ECE Installation
The first approach involves setting up a completely new ECE installation on your new infrastructure. Here’s a detailed guide on how to accomplish this:
Step 1: Set Up a New ECE Instance
Begin by installing a new ECE instance on your new infrastructure. Ensure that your new environment meets all the necessary requirements and configurations.
Step 2: Migrate Data
Method 1: Snapshot and Restore
One method to transfer your data is through Elasticsearch snapshots. This involves taking snapshots of your current deployments and restoring them in the new ECE installation.
- Create Snapshots: Utilize the snapshot API to capture the state of your Elasticsearch indices from your original deployment.
- Transfer Snapshots: Move these snapshots to your new ECE environment.
- Restore Snapshots: Use the restore API to load these snapshots into the new deployment.
Method 2: Cross-Cluster Replication
Alternatively, you can use cross-cluster replication to continuously replicate your data from the old to the new deployment. This method ensures data availability throughout the migration process.
- Set Up Cross-Cluster Replication: Configure replication between your old and new clusters.
- Monitor Replication: Ensure all data is successfully replicated before decommissioning the old deployment.
Step 3: Migrate ECE Configurations
Migration of ECE configurations, such as deployment templates, is not automatic. You can retrieve these configurations using the ECE API and apply them to your new installation.
- Retrieve Configurations: Use the ECE API to extract configuration details from your old installation.
- Apply Configurations: Utilize the ECE API to set up these configurations in your new installation.
Step 4: Update Deployment Endpoints
Ensure that your deployment endpoints are correctly updated. If you use aliases, configure them appropriately in both the original and new installations to avoid endpoint changes.
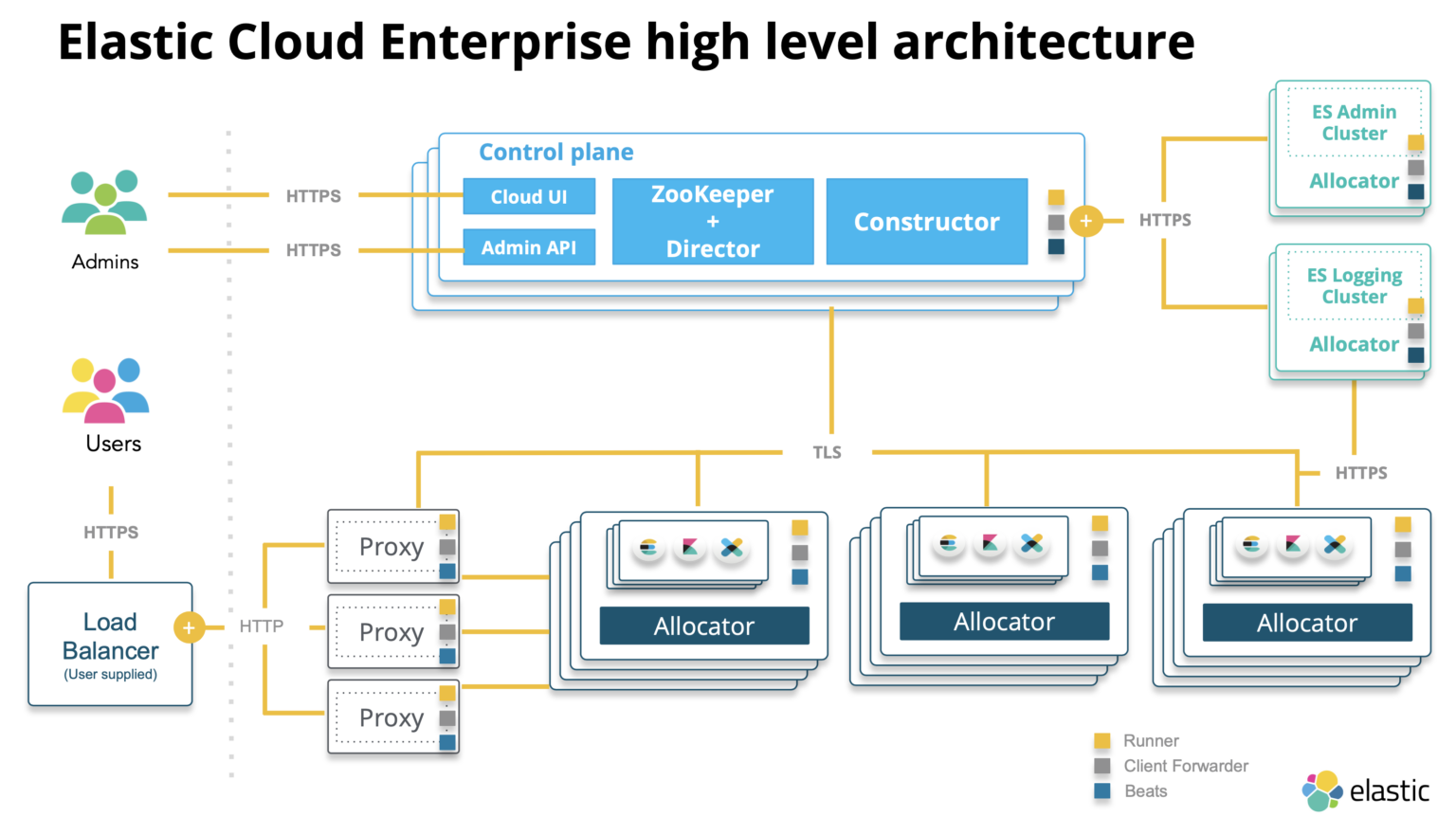
Option 2: Extending ECE Installation Across Data Centers
The second approach involves extending your current ECE installation across both the original and new data centers, followed by decommissioning the original hosts. This option requires a low-latency network connection between the data centers. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Set Up New Proxy Hosts
- Create New Proxy Hosts: Implement necessary load balancer changes to point to the new proxy hosts.
- Remove Old Proxy Hosts: Follow the delete host instructions to remove the old proxy hosts.
Step 2: Set Up New Allocators
- Create New Allocators: Set up new allocator hosts in the new data center.
- Delete Original Allocators: Follow the delete host instructions, which include putting hosts in maintenance mode, moving nodes off the hosts, and finally deleting the hosts.
Step 3: Set Up New Director Hosts
- Prepare and Install ECE on New VMs: Set up new director hosts on the new infrastructure.
- Verify Zookeeper Sync Status: Ensure that the Zookeeper sync status is correct.
- Decommission Old Directors: One-by-one, decommission the old director hosts after verifying the Zookeeper sync.
Step 4: Transition Coordinator and Proxy Hosts
- Add New Coordinator and Proxy Hosts: Set up new coordinator and proxy hosts on the new infrastructure.
- Remove Old Coordinator and Proxy Hosts: Follow the delete host instructions to remove the old coordinator and proxy hosts.
Step 5: Manage Hosts with Shared Roles
If your hosts have shared roles (e.g., a director also serving as a coordinator), manage these roles correctly. Add the new roles on the new hosts and remove them from the old hosts before decommissioning.
Step 6: Ensure Availability of Snapshots
Ensure that snapshots are available for all deployments before starting the migration. This precaution is crucial in case of any issues, such as problems with the Zookeeper quorum. If necessary, you can recover deployments from snapshots.
Conclusion
Migrating your ECE clusters to new infrastructure can be a complex but manageable process with careful planning and execution. Whether you create a new ECE installation or extend your existing one, following these steps will help ensure a smooth transition with minimal downtime and data integrity. Always ensure snapshots are available and verify configurations at every stage to prevent data loss and ensure continuity.
By adhering to these recommended practices, you can successfully migrate your ECE clusters to new infrastructure, leveraging enhanced hardware capabilities and meeting your organization’s evolving requirements